
What happens if you see a lynx and turn on the "cry of a wounded hare" right in the car? It was good that the window was closed.
Post: 21 May 14:49

Post: 21 May 14:49

Post: 25 September 19:44

Post: 14 February 13:05

Post: 30 January 00:19
Post: 28 January 00:57
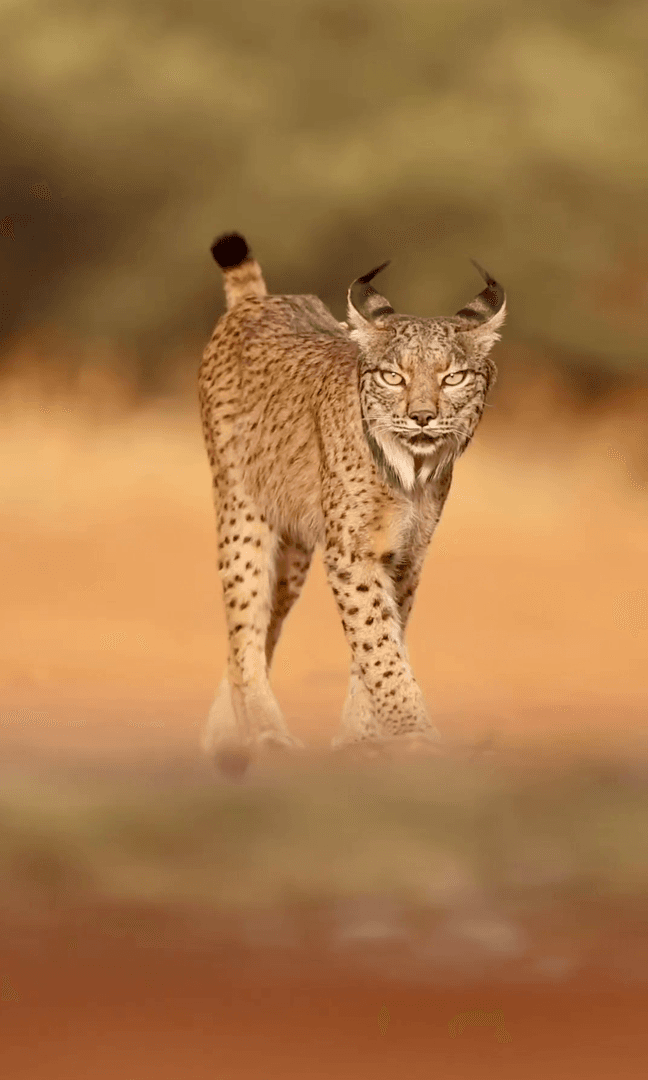

Post: 11 January 19:38

Post: 17 April 05:59

Post: 25 May 17:08

Post: 19 May 14:41

Post: 16 May 11:05

Post: 14 May 11:40

Post: 13 May 14:32

Post: 12 May 21:15

Post: 9 May 17:07

Post: 9 May 16:59